This page provides basic information on funds available to address desertification, land degradation, climate change, and drought. Furthermore, it highlights available international financial sources to promote positive development for combating desertification in the Sahel and the Horn of Africa region.
※ The views or information provided on this page is based on knowledge of AI-CD secretariat and we do not guarantee its credibility.Therefore, we highly recommend you to check the latest information from each funding agency.
Introduction
Major Activities in Seeking Finance

Finding financing can be challenging, but it is important to secure international fund in order to implement projects. We have listed the major activities below which you may consider when you seek finance.
1. Information and Data Collection
2. Survey and Research
3. Policy and Strategy Development
4. Institution / Organization Building
5. Infrastructure, Facility and Equipment Investment
6. Knowledge Sharing/Management
7. Capacity Building and Dissemination
8. Project Implementation and Management
9. Project Monitoring & Evaluation
Applying bodies for funds can be: Central Government, Local Government, CSOs / NGO, Community, and Private Sector Firm
Funding Agencies & Partners

There are varieties of funding agencies and partners which provide funds related to climate change, environment, soil degradation, combatting desertification. Firstly, they can be classified by types of funding agencies as follows.
1. International Public Donors
◆ Organizations under the United Nations (UN)
– United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
– United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
– United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)
– Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
◆ Other International Funding Agencies
– Global Environment Facility (GEF)
– GEF Small Grants Programme (GEF SGP)
– Green Climate Fund (GCF)
◆ Multilateral Development Banks
– World Bank
– African Development Bank
◆ Bilateral Agencies
– Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA)
– Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit GmbH (GIZ)
– Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA)
– United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
2. Financial Institutions
◆ Banks, Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)
◆ Crowdfunding Institutions
◆ Venture Capitals
3. Private Sector Corporates
4. Private Foundations
◆ Bill Gates Foundation
Major Funding Sources

The suitable funding sources are different by applying bodies and types of projects.
1. Public Sector Projects
There are two types of Public Sector Projects.
The first one is a project directly financed by international donors as a part of their own lending programs based on their country strategy for the benefit for the country government and/or community concerned, and the second one is a project financed through a project to which the concerned country government and/or community can assume a role as the executing agency.
◆ By International Donors
– Global Environment Facility (GEF)
– Green Climate Fund (GCF)
– Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO)
– International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD)
◆ Through International Donors
– World Bank Group (WBG)
– African Development Bank (AfDB)
– United National Environment Program Finance Initiatives (UNEP-FI)
2. Community Projects by International Donors
– GEF Small Grant Program (GEF-SGP)
– Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit GmbH (GIZ)
– Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), Grass Roots Project
3. Community and Private Sector Projects by Private Sector Institutions and NGOs
– Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)
– Foundations
– NGOs
Major Funding Organizations
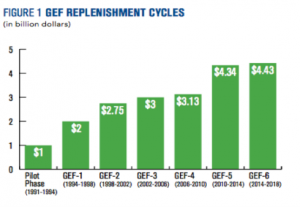
Global Environment Facility (GEF)
GEF was established on the eve of the 1992 Rio Earth Summit to help tackle our planet’s most pressing environmental problems. GEF has 183 member countries in partnership with international institutions, civil society organizations (CSOs), and private sector to address global environmental issues, and national sustainable development initiatives. GEF is the largest public funder of projects to improve the global environment. Financial contributions are replenished every four years. ※ For more information, please check Global Environment Facility
GEF SGP
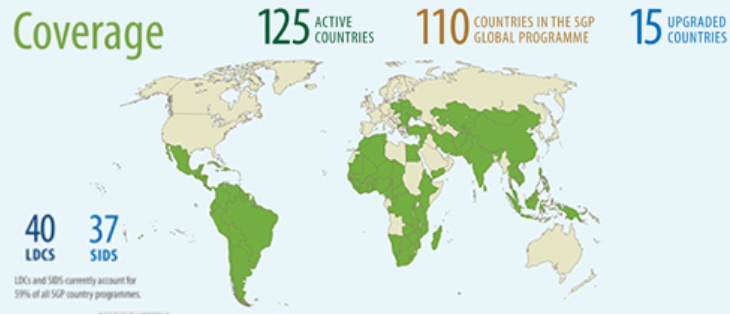
GEF Small Grants Programme (GEF SGP) was established in 1992, the year of Rio Earth Summit embodying the very essence of sustainable development by “thinking globally acting locally”. It provides financial and technical support to projects that conserve and restore the environment while enhancing people’s well-being and livelihoods. SGP grants are made directly to community-based organizations (CBOs) and/or non-governmental organizations (NGOs) in recognition of the key role they play as a resource and constituency for environment and development concerns. The maximum grant amount per project is US$50,000 (but averages around US$25,000). ※ For more information, please check the GEF Small Grants Programme
Green Climate Fund (GCF)
The Green Climate Fund (GCF) is a fund established at Inchon, Korea in 2000 within the framework of the UNFCCC with a view to assisting developing countries in adaptation and mitigation practices to counter climate change. GCF does not function properly still due to the issues on the fund’s Business Model Framework (BMF). They identified the need to assess various options for how nations could access the fund due to the lack of Stakeholders’ involvement. JICA has become an Accredited Entity (AE). ※ For more information, please check The Green Climate Fund.
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) is a UN specialized agency leading international efforts to defeat hunger. FAO is also a source of knowledge and information and helps developing countries in transition modernize and improve agriculture, forestry and fisheries practices with its 194 member states. FAO support implementation of UNCCD in order to increase resilience to climate change and drought through the promotion of Sustainable Land Management practices as a means to improve people’s livelihoods. International Fund for Agricultural Fund (IFAD) enabling the rural poor to overcome poverty with a broad range of financing tools. ※ For more information, please check the Food and Agriculture Organization
.
World Bank Group (WBG)
World Bank Group (WBG) was established in 1945 and headquartered in Washington, D.C., USA. World Bank Group is comprised by International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), International Development Association (IDA), International Finance Corporation (IFC), Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) and International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID). And IDA is an agency to offer interest rate free credit. Country Partnership Framework (CPF, or Country Assistance Strategy, in the past) are formulated every 4 years. Desertification, Land Degradation, and Drought issues are often dealt in CPF. Policy Development to Capacity Building is possible to be included in CPF. ※ For more information, please check the World Bank Group
African Development Bank (AfDB)
AfDB is headquartered in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire. AfDB is comprised of AfDB and African Development Fund (ADF) which is an agency to offer interest rate free credit. Country Strategy Paper (CSP) are formulated every 4 years. Desertification, Land Degradation, and Drought issues are often dealt in CSP. Policy Development to Capacity Building is possible to be included in CSP. ※ For more information, please check the African Development Bank
United Nations Environment Program – Finance Initiative (UNEP FI)
United Nations Environment Program – Finance Initiative (UNEP FI) is a partnership between UNEP and global financial sector created in the context of the 1992 Earth Summit UNEP FI, with a mission to promote sustainable finance. Over 200 financial institutions, including banks, insurers, and investors, work with UNEP. ※ For more information, please check the United Nations Environment Program.
Climate and Development Knowledge Network (CDKN)
CDKN is an initiative formed in 2010, to link developing countries with experts on climate change. CDKN adapts to consequences of climate change and builds capacity for a low-carbon economy. CDKN does this by combining research, advisory services, and knowledge management in support of locally owned and managed policy processes. CDKN works across Africa, Asia and Latin America and the Caribbean, with a focus on 12 priority countries. In Africa, they are Kenya, Rwanda, Ethiopia, and Uganda. ※ For more information, please check the Climate and Development Knowledge Network
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
GIZ is an international development assistance agency of Germany funded fully by its government. Sector Project to Combat Desertification combines advice on policy, strategy and technical issues and operates in three action areas:
– Advising on policy and strategy concerning UNCCD processes
– Organizing and disseminating knowledge and experience relating to sustainable land management, and advising on the implementation of measures to combat desertification
– Hosts the Economics of Land Degradation (ELD) Initiative’s Secretariat
※ For more information, please check the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit.










